Mailing List Verifing Window
Address checking involves three steps:
●processing of the source file
●saving of the results into the output files
●release of the resources allotted to the program on the first step
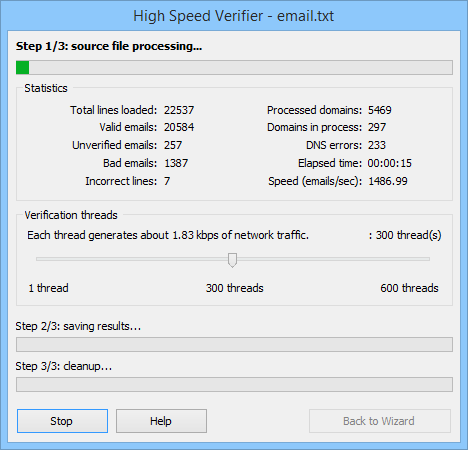
Step 1/3: source file processing.
Progress of the process is displayed by indicators in the Statistics window:
●Total lines loaded — the number of lines loaded from the source file. Some of those lines are already processed, others are under processing — DNS servers are queried about addresses from those lines.
●Valid emails — number of addresses that were checked and found valid.
●Unverified emails — the number of addresses that proved impossible to check (see "Technical Description of Operation").
●Bad emails — addresses that were checked and found invalid.
●Incorrect lines — number of lines with wrong address syntax. When saving the results, HSV saves those addresses in the file with invalid addresses.
●Processed domains — number of unique mail domains processed. A list might contain many addresses from same domains, therefore this indicator normally shows a number smaller than the total number of valid, invalid, and unchecked addresses.
●Domains in process — number of domains being inquired about from DNS servers at the moment. This number can be changed by the thread number control slider (see below).
●DNS errors — number of errors occurred when querying DNS. It is supposed that a DNS server must answer whether there are servers receiving mail for particular domain or not (see "Address Verification Technologies"). However, DNS often is unable of giving the reply because a server that stores information for the domain queried about is inaccessible, so it returns an error message. Moreover, HSV makes several attempts at checking such address via different DNS servers from the list, so one "unstable" address increases the number of errors by more than one. Errors may also occur due to overload of your Internet-connection (e.g. because of exceeded thread number). It is considered normal if the error counter shows a number three to four times smaller than the number of processed domains. Otherwise, see "Diagnostics and Optimization".
●Elapsed time — time elapsed from start of the current checking session, in the format HH:MM:SS.
●Speed (emails/sec) — shows average speed of address checking in the past 30 seconds. When the source file checking is about to be completed, readings of this indicator usually drop down to less than 10 or even to less than 1. This happens because some domains which first check failed remain in the task list, and HSV attempts at checking those domain through other servers. Checking of the last domains sometimes takes 1..3 minutes.
Under the Statistics window, there is a slider that controls the number of simultaneous queries to DNS servers (or the number of threads). You can set the tread number from 1 to 600. If 600 threads are used, 600 domains are checked simultaneously, and HSV sends up to 15000 queries to DNS servers per minutes, with the peak network traffic up to 700 kbps.
Depending on the result of you DNS server list testing, High Speed Verify calculates approximate width of the network channel required for each thread and shows it above the slider.
If you are going to run HSV with more than 50 threads, you ought to thoroughly read the article "Technical Description of Operation". Inconsiderate increase of the thread number might result not in greater operation rate of the program but in greater number of errors and significant reduction of the operation rate. In some networks, if the list of DNS-servers is small, great number of threads might result in rejection of queries from other users by DNS servers, which would cause failure or even collapse of the network. Also please read the article "Diagnostics and Optimization".
Step 2/3: Saving of the Results.
On this step, HSV saves the check results on a disc. The data to be saved are first stored in a temporary file. That's why name of any output file may be similar to name of the source file: the results will be placed in a temporary file first, and upon completion of the check, the source file will be replaced with the temporary file. For this reason you can also safely terminate HSV operation on the second step of checking process (the result saving step) – the results will be lost, but there absolutely no risk that the source file will be damaged. For more details see the article "Source and destination files window".
Step 3/3: Cleanup.
The third step, release of the allotted system resources, is a required action, which cannot be interrupted or cancelled. This step will be performed even if the first or the second step was terminated. On this step, HSV frees memory allotted to store intermediate results.
